The Pick Fill Seal machine, known as form-fill-seal (FFS) machines, are sophisticated automated packaging systems widely used in various industries, including food, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods.
As a leading global Pouch packing machine manufacturer of these machines, we take pride in delivering cutting-edge packaging solutions. This article will explain in detail how PFS machines work, their key components, and the principles behind their operation.
The Principle Behind Premade Pouch Filling Machine
A Pouch packing machine operates on a straightforward yet highly efficient principle, combining multiple packaging steps into a single, streamlined process:
- Pick: The pouch packaging machine accurately picks preformed pouches from a magazine or pouch feeder. This process is typically automated using vacuum or mechanical grippers.
- Fill: Once the pouch is in position, the filling system dispenses the product into the pouch. The filling method depends on the product type and can involve volumetric, gravimetric, or liquid filling systems.
- Seal: The filled pouch is then sealed hermetically using heat sealing technology. This involves applying heat and pressure to the pouch’s film to create a strong, airtight seal.
Suggested Read:
- 10 Benefits of Investing in a High-Quality Liquid Packaging Machine
- Top 5 Premade Pouch Packing Machine Brands in 2024
Key Components of PFS Machines:
PFS machines, or Pick, Fill, and Seal machines, are automated systems used in various industries for packaging products. They typically consist of a filling mechanism, a stoppering unit, and a plunger for sealing, and often include a labeling and inspection section.
- Pouch Feeder: Ensures a continuous supply of pouches to the machine.
- Pick and Place Mechanism: Precisely picks up and positions pouches for filling.
- Filling System: Dispenses the product into the pouch accurately and efficiently.
- Sealing System: Creates a secure and airtight seal on the filled pouch.
- Conveyor System: Transports pouches through the machine.
- Control System: Manages the entire process, including speed, accuracy, and product parameters.
- Film Roll Holder: Holds the roll of packaging material (for machines that form pouches).
- Former or Collar: Shapes the flat film into a tube or package shape (for form-fill-seal machines).
- Cutting Mechanism: Separates individual packages (for continuous form-fill-seal machines).
Suggested Read:
- 7 Common Mistakes to Avoid in Ointment Manufacturing Plant
- 8 Strategies for Growing Your Income with a Liquid Manufacturing Plant
Types of Pick Fill Seal Machines:
Pick Fill Seal machines come in various types, primarily categorized as linear and rotary. Linear machines handle products sequentially, while rotary models process multiple pouches simultaneously, increasing production speed. The choice depends on production volume, product type, and desired output.
- Vertical Form-Fill-Seal (VFFS):
- Ideal for producing pillow bags, gusseted bags, and stand-up pouches.
- Commonly used for snacks, grains, and powdered products.
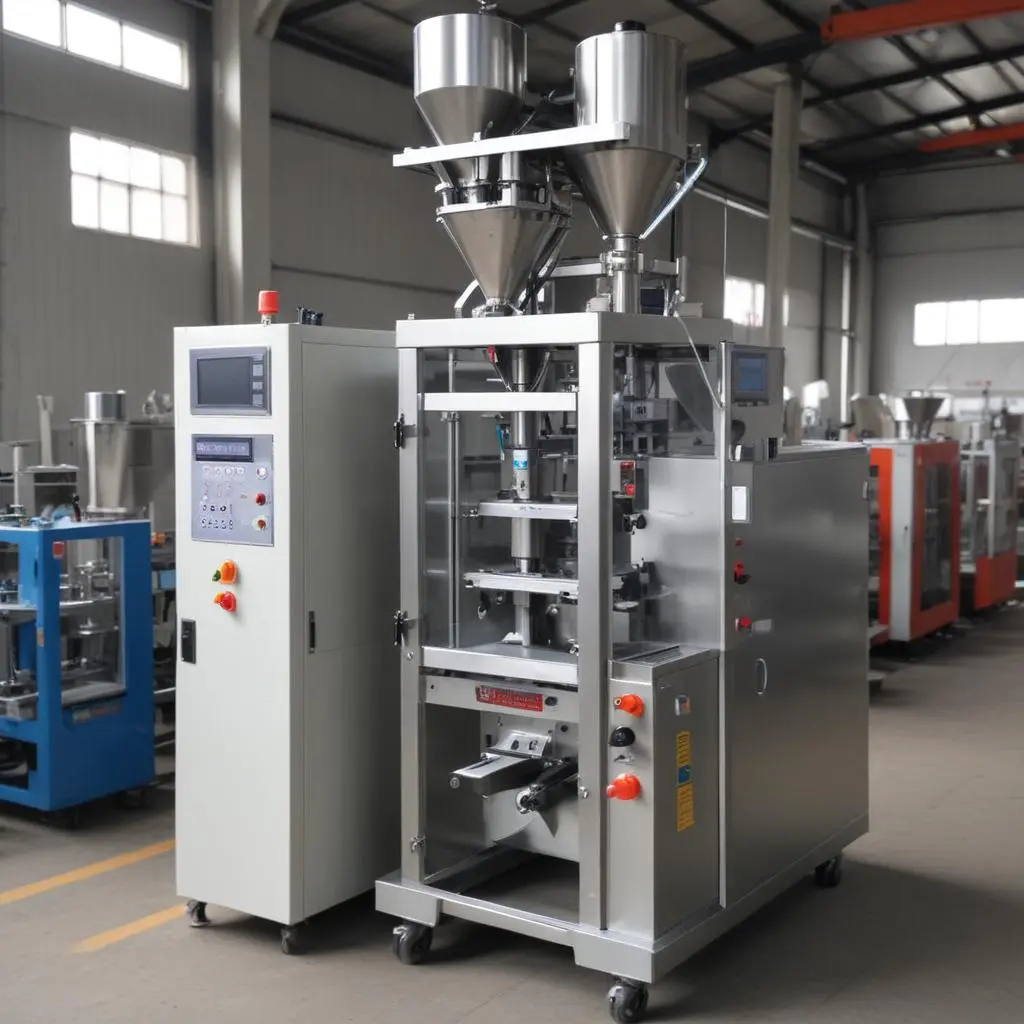

- Horizontal Form-Fill-Seal (HFFS) Machine:
- Suitable for thermoformed trays and blister packs.
- Often used for medical devices, fresh produce, and delicate products.
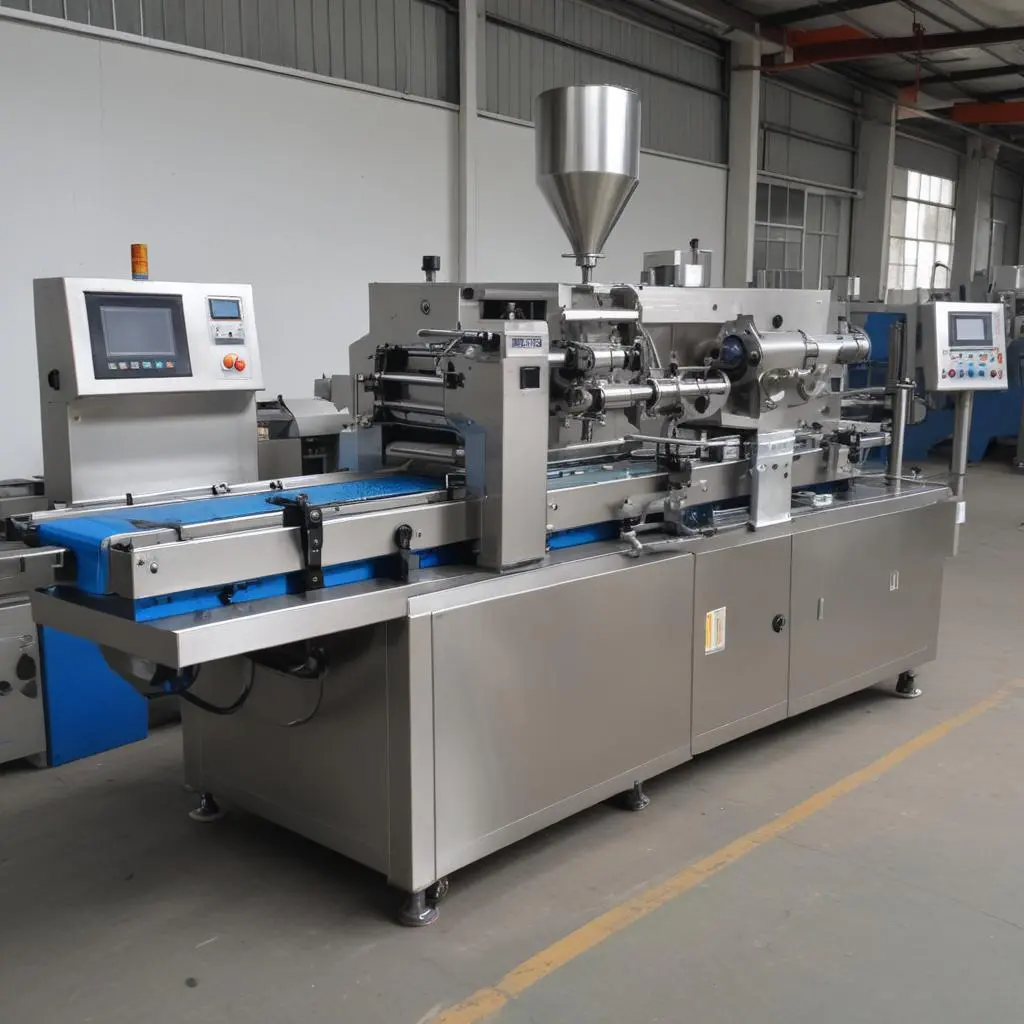

- Sachet Machines:
- Specialized VFFS machines for producing small, single-serve packets.
- Common in condiment and sample packaging.
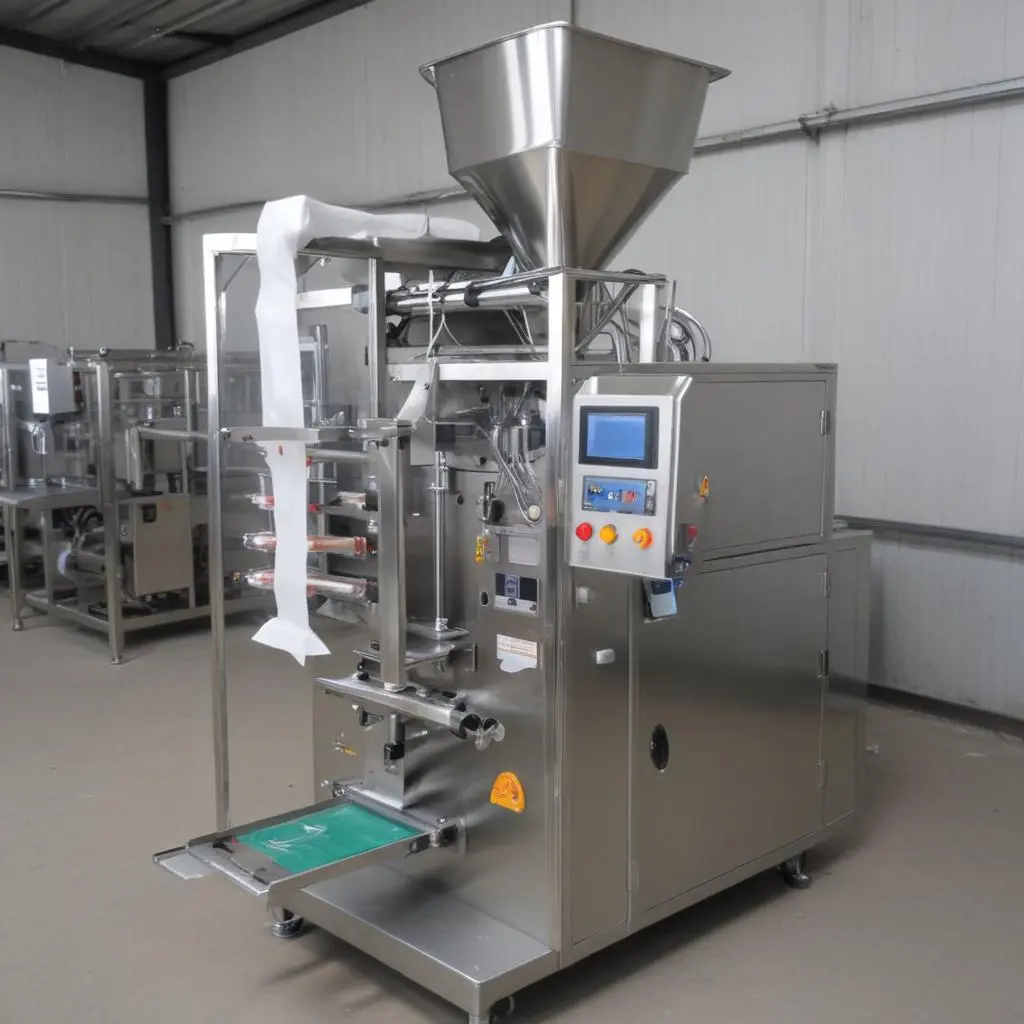

- Premade Pouch Filling Machines:
- Work with preformed pouches, focusing on the fill and seal steps.
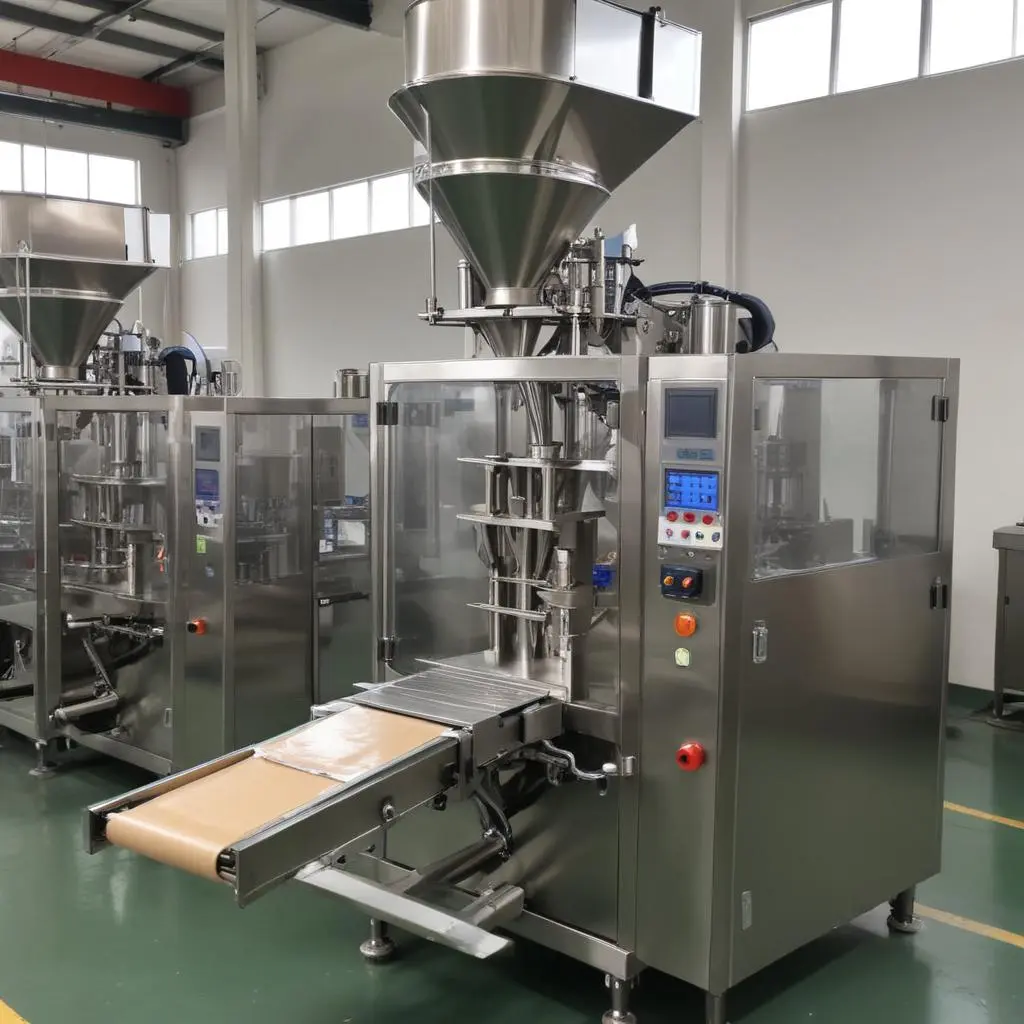

Detailed Process Breakdown:
PFS machines begin by unwinding packaging film from a roll and feeding it through rollers for tension control. The film is then shaped into a tube (VFFS) or individual pockets (HFFS), or pre-made pouches are picked up.
Products are dispensed into the formed package using methods like volumetric, weight-based, or count-based filling. The package is then sealed shut, often using heat sealing, and for continuous machines, the final package is separated.
- Film Feeding (for form-fill-seal machines):
- The machine unwinds the packaging film from a large roll.
- The film is guided through a series of rollers that control tension and alignment.
- Forming the Package:
- For VFFS machines, the film passes over a forming collar that shapes it into a tube.
- In HFFS machines, the film is formed into a series of pockets or trays.
- Pre-made pouch machines skip this step, using already-formed pouches.
- Creating the Initial Seal:
- In VFFS machines, the edges of the tube are sealed together to form a continuous vertical seal.
- HFFS machines may create an initial seal at the bottom of each pocket.
- Picking:
- This step involves picking up individual pouches from a magazine for pre-made pouch machines.
- The pick-and-place mechanism uses vacuum suction cups or mechanical grippers to handle pouches.
- Filling:
- The product is dispensed into the formed package or pouch.
- Filling methods vary based on the product:
- Volumetric filling for liquids
- Weight-based filling for solids or powders
- Count-based filling for discrete items
- Top Sealing:
- The top of the package is sealed, typically using heat sealing bars.
- Some machines use alternative sealing methods like ultrasonic sealing.
- Cutting (for continuous form-fill-seal machines):
- The sealed packages are separated by a cutting mechanism.
Key Technologies and Innovations:
PFS machines have benefited from significant technological advancements. Modern machines incorporate precision servo motors for accurate and consistent product handling. Advanced PLC controls offer flexibility and customization.
- Servo Motors: Provide precise control over machine movements, improving accuracy and speed.
- Advanced Control Systems: PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) or PC-based systems for enhanced automation and flexibility.
- Vision Systems: Cameras and sensors that inspect packages for defects or filling accuracy.
- Clean-in-Place (CIP) Systems: Allow for thorough cleaning of product contact areas without disassembly.
- Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP): Some machines can inject gases into packages to extend product shelf life.
Customization and Versatility:
PFS machines are designed to be highly versatile, and capable of handling a wide range of products and pouch types. Customization options include:
- Product type: Powders, granules, liquids, pastes, and more.
- Pouch size and shape: Flat, stand-up, zippered, and various custom designs.
- Filling accuracy: Precise dosing for optimal product quantity.
- Sealing options: Different seal types and patterns to meet packaging needs.
Advantages of Pick Fill Seal Machines:
PFS machines offer high speed and precision, significantly increasing packaging efficiency while minimizing product waste. They are versatile, handling various products and packaging formats, maintaining hygiene, and saving space compared to traditional packaging lines.
- Efficiency: Combine multiple packaging steps into one continuous process.
- Speed: Can produce hundreds of packages per minute.
- Consistency: Automated systems ensure uniform package quality.
- Flexibility: Many machines can handle various package sizes and styles.
- Hygiene: Enclosed systems reduce contamination risks.
- Cost-effectiveness: Reduce labor costs and material waste.
Considerations for Implementation:
- Product Compatibility: Ensure your product is suitable for the chosen machine type.
- Production Volume: Match machine capacity to your production needs.
- Packaging Material: Select the appropriate film or packaging material for your product and machine.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance is crucial for optimal performance and longevity.
- Training: Proper operator training is essential for efficient and safe operation.
Conclusion:
Premade Pouch Packing Machine or Pick Fill Seal machines are sophisticated yet user-friendly systems that have revolutionized the packaging industry. By understanding their basic principles and operations, businesses can make informed decisions about implementing these machines in their production lines, leading to increased efficiency and product quality. As technology continues to advance, Seal Packing Machine will undoubtedly plays an increasingly crucial role in modern manufacturing and packaging processes.