A GLIMPSE OF EACH INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION
The summary that follows is based on a study titled Industry 4.0 for pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Industry 1.0
The modern pharmaceutical industry’s starting point The manual processing of botanical, mineral, and animal-derived materials progresses from simple hand-operated equipment to commercial-scale machines capable of crushing, milling, blending, and pressing bigger quantities of medicines.
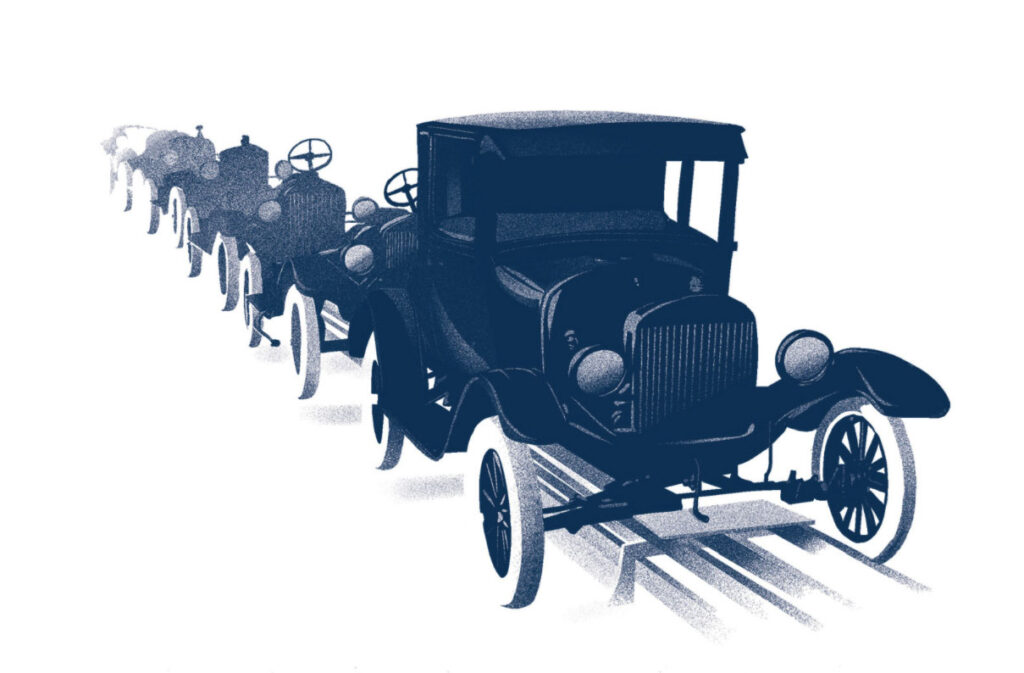


Industry 2.0
Adoption of electricity, as well as the first electronic machinery and production lines with pre-programmed controls Basic automation and Jocess controls, were incorporated, allowing producers to establish basic process parameters. Industry 2.0 sees the utilization of electronic machine-based crushing, milling, mixing, and tablet pressing, allowing for larger-scale manufacturing and, more crucially, process and quality monitoring.
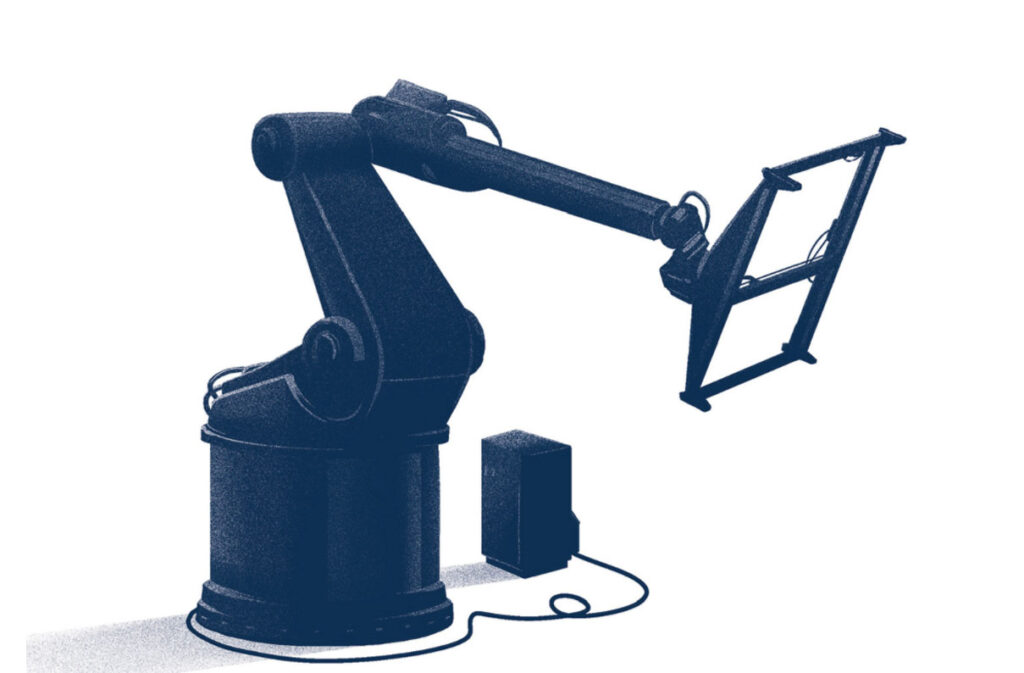
Industry 3.0
As a result of the advancement and accessibility of computer and communication technology
Technologies such as networked computing, the internet, and wireless communications enabled more automation of processes and equipment, enabling ideas such as continuous manufacturing and active control in pharma manufacturing.

Industry 4.0
Brings advanced manufacturing technologies together to create integrated, autonomous, and self-organizing production systems that work without human intervention.
The promise of Industry 4.0 is that whole production processes and infrastructures would be improved. In such a setting, performance data may be examined by algorithms and utilized to make vital real-time business and operational choices that have a direct influence on production outputs.


